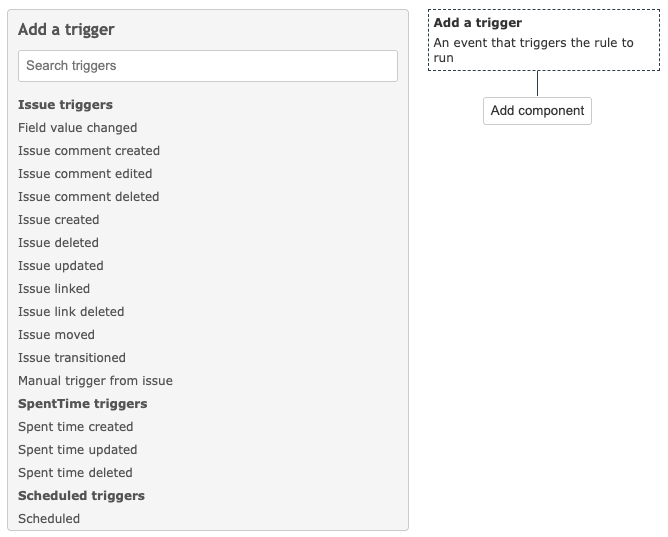
Automations are initiated by one or more triggers, which detect specific Redmine events. Every automation rule must start with a trigger and can then be combined with conditions, branches, and actions as needed. There are three groups of triggers:
- Issue triggers – related to Redmine task actions.
- Spent Time triggers – related to Redmine time entry actions.
- Scheduled triggers – start at a specific date and time and repeat at a predefined interval. It is crucial to combine these triggers with conditions for correct use.
Issue Triggers #
Issue triggers are related to task actions and changes. They fully cover the task lifecycle in Redmine and give users the opportunity to automate manual operations, enforce company business processes, and reduce errors.
In this section, we describe and provide a detailed settings guide for each Issue trigger.
Field Value Changed #
Activated when a specific issue field (e.g., status, priority) changes.
Settings:
- Fields to monitor for changes – user selects which fields are monitored.
- Change type – user defines the type of change in the field.
Fields to monitor for changes – possible values:
- Tracker
- Project
- Subject
- Description
- Status
- Priority
- Assignee
- Target version
- Start date
- Due date
- Estimated time
- Closed
- Category
- Custom fields
One or multiple fields can be selected.
Change type – possible values:
- Any change to the field value – any change in the selected field(s) triggers the automation rule.
- Value added – only when a value is added will the automation be triggered. Removing or changing a value will not trigger the rule.
- Value deleted – only when a value is deleted will the automation be triggered. Adding or changing a value will not trigger the rule.
For all selected fields, one change type is applied.
Issue Comment Created #
Triggered when a new comment is added to an issue.
This trigger needs no configuration. It will trigger an automation rule every time a comment is added to a task. We recommend combining this trigger with a condition to look for specific tasks, or creating the automation rule for a specific project only.
Example implementation:
- Trigger: Issue comment created.
- Condition: Tracker is Support.
This combination runs automation when a new comment is added to a task with tracker “Support”.
Issue Comment Edited #
Triggered when an existing comment is modified.
This trigger needs no configuration. It will trigger an automation rule every time a comment is edited on a task. We recommend combining this trigger with a condition to look for specific tasks, or creating the automation rule for a specific project only.
Example implementation:
- Trigger: Issue comment edited.
- Condition: Tracker is Support.
This combination runs automation when an existing comment is edited on a task with tracker “Support”.
Issue Comment Deleted #
Triggered when a comment is removed from an issue.
This trigger needs no configuration. It will trigger an automation rule every time a comment is deleted on a task. We recommend combining this trigger with a condition to look for specific tasks, or creating the automation rule for a specific project only.
Example implementation:
- Trigger: Issue comment deleted.
- Condition: Tracker is Support.
This combination runs automation when an existing comment is deleted on a task with tracker “Support”.
Issue Created #
Fired upon the creation of a new issue.
This trigger needs no configuration. It will trigger an automation rule every time a task is created. We recommend combining this trigger with a condition to look for specific tasks, or creating the automation rule for a specific project only.
Example implementation:
- Trigger: Issue created.
- Condition: Tracker is Bug.
- Condition: Priority is Urgent.
This combination runs automation when a new task with tracker “Bug” and priority “Urgent” is created.
Issue Deleted #
Activated when an issue is deleted.
This trigger needs no configuration. It will trigger an automation rule every time a task is deleted. We recommend combining this trigger with a condition to look for specific tasks, or creating the automation rule for a specific project only.
Example implementation:
- Trigger: Issue deleted.
- Condition: Due date in more than 1 day(s).
This combination runs automation when a task with a due date in the future is deleted.
Issue Updated #
Triggered for any update to issue properties.
This trigger needs no configuration. It will trigger an automation rule every time a task is updated. We recommend combining this trigger with a condition to look for specific tasks, or creating the automation rule for a specific project only.
Example implementation:
- Trigger: Issue updated.
- Condition: Priority is Immediate.
This combination runs automation when a task is updated and priority is “Immediate”.
Issue Linked #
Occurs when an issue is linked to another issue.
Setting:
- Link types – user selects the link type to watch for.
Possible values:
- Related to
- Is duplicate of
- Has duplicate
- Blocks
- Blocked by
- Precedes
- Follows
- Copied to
- Copied from
One or multiple values can be selected.
Issue Link Deleted #
Triggered when an issue link is removed.
Setting:
- Link types – user selects the link type to watch for.
Possible values:
- Related to
- Is duplicate of
- Has duplicate
- Blocks
- Blocked by
- Precedes
- Follows
- Copied to
- Copied from
One or multiple values can be selected.
Issue Moved #
Fired when an issue is moved between projects.
Settings:
- Source project – project the task is moved from.
- Target project – project the task is moved to.
Possible values:
- Source project: all open projects in the system.
- Target project: all open projects in the system.
One value can be selected per setting.
Issue Transitioned #
Activated on workflow status transitions.
Settings:
- From status – status the task transitions from.
- To status – status the task transitions to.
Possible values:
- From status: all statuses in the system.
- To status: all statuses in the system.
One or multiple values can be selected.
Manual Trigger from Issue #
User-initiated; available as a button or menu item on the issue view. The settings define where the manual trigger will be shown and which users can see it.
Settings:
- Trackers – trackers on which the manual trigger is shown.
- Users – users who will see the manual trigger.
- User groups – groups of users who will see the manual trigger.
- User roles – roles that will see the manual trigger.
Possible values:
- Trackers: all trackers in the system. Leaving this field empty selects all trackers.
- Users: all users in the system. Leaving this field empty selects all users.
- User groups: all user groups in the system. Leaving this field empty selects all groups.
- User roles: all user roles in the system. Leaving this field empty selects all roles.
One or multiple values can be selected.
Spent Time Triggers #
Spent time triggers are related to time entry actions and changes. They fully cover the spent time lifecycle in Redmine and give users the opportunity to automate manual operations, enforce company business processes, and reduce errors.
In this section, we describe and provide a detailed settings guide for each Spent Time trigger.
Spent Time Created #
Fired when a new time entry is logged.
This trigger needs no configuration. It will trigger an automation rule every time a time entry is created. We recommend combining this trigger with a condition to look for specific time entries, or creating the automation rule for a specific project only.
Example implementation:
- Trigger: Spent time created.
- Condition: Priority is Low.
This combination runs automation when a time entry is created and the related task has low priority.
Spent Time Updated #
Activated on modification of an existing time entry.
This trigger needs no configuration. It will trigger an automation rule every time a time entry is updated. We recommend combining this trigger with a condition to look for specific time entries, or creating the automation rule for a specific project only.
Example implementation:
- Trigger: Spent time updated.
- Condition: Tracker is Bug.
This combination runs automation when a time entry is updated and the related task has tracker “Bug”.
Spent Time Deleted #
Fired when a time entry is removed.
This trigger needs no configuration. It will trigger an automation rule every time a time entry is deleted. We recommend combining this trigger with a condition to look for specific time entries, or creating the automation rule for a specific project only.
Example implementation:
- Trigger: Spent time deleted.
- Condition: Status is Done.
This combination runs automation when a time entry is deleted and the related task has status “Done”.
Scheduled Triggers #
Scheduled triggers are time-based triggers automatically run by the system according to the settings. They allow users to create time-driven automation.
In this section, we describe and provide a detailed settings guide for Scheduled triggers.
Scheduled #
Automations can be set to run on a defined schedule (e.g., daily, weekly).
Settings:
- Every – defines how often the trigger is executed by the system.
- Next run at – defines the first run of the automation.
Every – possible values:
- Minutes
- Hours
- Days
- Weeks
- Months
Next run at – possible values:
- Date and time (single value can be selected)
